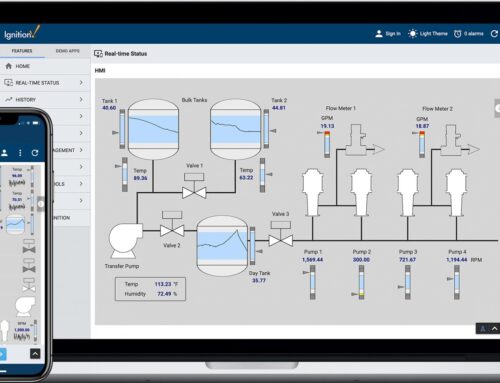
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, digital twins are transforming how manufacturers visualize, analyse, and optimize their operations. Leveraging Inductive Automation’s Ignition platform alongside robust programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) offers a powerful approach to building these sophisticated virtual replicas of physical assets. A digital twin serves as a dynamic, real-time digital counterpart of a physical entity in the manufacturing world, enabling you to simulate processes, predict equipment failures, and enhance maintenance strategies with unparalleled accuracy.
Through this article, we aim to provide manufacturers and plant managers with a comprehensive guide to building a digital twin using Ignition and PLC data. Our insights draw on decades of experience in the design, deployment, and support of Ignition solutions, placing Innorobix at the forefront of this innovative technology.
Key Insights:
- Understanding Digital Twins: Explore the core benefits of implementing a digital twin in yoru manufacturing operations, from improved predictive maintenance to enhanced product lifecycle management.
- The Role of Ignition and PLCs: Learn how Ignition’s scalable and versatile platform, combined with real-time data from PLCs, acts as the backbone for your digital twin architecture.
- Real-World Applications: Discover case studies where digital twins have revolutionized manufacturing processes, from reducing downtime in heavy machinery to optimizing production lines in complex manufacturing environments.
- Steps to Deployment: Gain a step-by-step overview of deploying an Ignition-based digital twin, covering everything from data acquisition and integration to visualization and analytics.
- Overcoming Challenges: Analyze common deployment pitfalls and strategic approaches to navigating these challenges, ensuring a successful implementation of your digital twin.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of constructing a digital twin with Ignition and PLCs, empowering your facility with actionable intelligence and operational excellence.
Understanding the Role of PLC Data in Creating Digital Twins with ignition
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) data plays a pivotal role in the creation of digital twins within the Ignition SCADA platform. By acting as the primary source of real-time operational data, PLCs enable manufacturers to construct accurate and dynamic digital replicas of their physical assets and processes. These digital twins use live data from plcs to mirror the behavior, state, and performance of their real-world counterparts, allowing for improved monitoring and optimization. For instance, in a manufacturing plant producing automotive parts, the live data from the PLC controlling the stamping machine can be integrated into Ignition to create a digital twin. This twin not only visualizes real-time operational conditions such as motor speed or press force but also assists in predictive maintenance by alerting operators to deviations that coudl indicate a pending failure. The seamless connectivity between Ignition and PLCs ensures that digital twins updated in real time are aligned closely with physical operations.
Creating digital twins using PLC data in Ignition is not just limited to enhancing visibility but also in driving strategic value through advanced analytics and simulation. System integrators leverage PLC data to develop models within Ignition that simulate ’what-if’ scenarios, examining potential process modifications before implementing them physically.Such as, a production line aiming to increase throughput may use a digital twin to simulate the effect of adjusting conveyor speeds or modifying heat treatment times. These simulated adjustments, driven by existing and historical PLC data, enable managers to make informed decisions that optimize production and minimize downtime. Key to the success of these initiatives is ensuring high-quality, accurate data from PLCs, as poor data synchronization or latency issues can lead to inaccurate digital representations. Ignition’s architecture supports robust data handling capabilities, with features like Tag Historian to ensure data integrity and availability, fostering dependable and scalable digital twin projects.
Leveraging Ignitions Built-In Tools to Enhance Digital twin Accuracy and Functionality
Ignition provides an extensive suite of built-in tools designed to enhance the precision and capabilities of digital twins in manufacturing environments.Tag Historian,Transaction groups,and Realtime Tag Providers are foundational features that facilitate seamless integration and processing of PLC data within your digital twin models. By efficiently managing large streams of data, Tag Historian offers historical context that allows for predictive modeling and in-depth analysis, while Transaction Groups automate the movement of data, ensuring that all relevant parameters are incorporated into the digital twin without manual intervention. This real-time data flow is crucial for keeping digital twin models dynamic and reflective of the physical process’s current state.
To illustrate, consider a manufacturing plant where predictive maintenance is pivotal. By leveraging Ignition’s Scripting and Python capabilities,engineers can develop custom scripts to create simulation models that predict equipment failures. These real-time predictive insights enable plant managers to anticipate and mitigate potential downtimes. Moreover, Ignition’s integrated Visualization tools, through its HMI/SCADA interface, afford engineers the ability to visualize digital twins on interactive dashboards, making complex data more accessible and actionable. This holistic approach not only maximizes sensor and PLC data utility but also amplifies critical decision-making processes by providing a comprehensive digital replica of plant operations.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Digital Twin Implementation with Practical Solutions
Deploying a digital twin in a manufacturing environment ofen introduces several challenges that can hinder successful implementation. One common obstacle is the integration of disparate data sources. Manufacturers typically utilize data gathered from various PLCs, sensors, and production equipment, and amalgamating this information into a cohesive platform can be complex. Using Ignition, however, offers a streamlined approach to overcoming this hurdle. Its decentralized architecture allows for seamless integration with a variety of PLCs and data formats, ensuring real-time synchronization. As a notable example, a leading automotive parts manufacturer successfully utilized Ignition to connect their existing Allen-Bradley PLCs and Siemens SIMATIC PLCs into a unified digital twin model, thus enhancing their process monitoring capabilities.
Another significant challenge in digital twin implementation is ensuring data reliability and accuracy. When leveraging a production system’s data, ensuring the consistency and integrity of this data is crucial. Ignition’s historian module and its robust tag system provide tools to maintain high data quality. These features not only archive data but also allow users to set up alerting and reporting mechanisms to detect anomalies. Consider how a food and beverage plant used Ignition to track temperature variations across their cooling systems, implementing alerts for deviations that could indicate equipment failure. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and maintains product quality,showcasing the practical application and reliability of a digital twin powered by Ignition.
Expert Insights and Best Practices for Maximizing ROI with Digital twin Technology in Ignition
One of the moast strategic moves manufacturers can make with Ignition SCADA is to leverage digital twin technology to improve operational efficiencies and unlock new insights. A digital twin utilizes real-time PLC data to create a virtual replica of physical equipment and processes. This provides plant managers with a predictive lens through which they can identify potential failures before they occur, optimize maintenance schedules, and enhance decision-making. For instance, by continuously monitoring data from a conveyor system’s motors and sensors, managers can foresee wear and tear factors that, if unchecked, could lead to downtime. By acting preemptively, this not only minimizes unexpected halts but also maximizes system efficiency and resource allocation.
to ensure you harness the full ROI potential of digital twin technology within Ignition, consider the following best practices:
– Data Integration: Seamlessly integrate data from disparate sources to provide a holistic view.- Dynamic Modeling: Ensure the digital twin model is flexible and adapts to changes in real-time, reflecting the ever-evolving factory floor conditions.
– User-Friendly Interfaces: Equip operators and managers with intuitive dashboards that require minimal training.
– Scalability: Plan for scalability from the onset. As systems grow or change, the digital twin must remain relevant.
By heeding these practices, Innorobix ensures the deployment of Ignition’s capabilities is both seamless and forward-thinking, putting your operation at the cutting edge of industrial innovation.
Q&A
Q: What exactly is a Digital Twin, and how does it benefit industrial automation using Ignition?
A: A Digital Twin is a virtual representation of a physical system or process used in factories and manufacturing environments. Utilizing Ignition SCADA, a Digital Twin can:
- Enhance Real-Time Monitoring: Translates real-world data from PLCs into a digital model.
- Improve Predictive Maintenance: Anticipates equipment failures by analyzing trends in operational data.
- Optimize Performance: Enables simulation of different conditions to identify improvements in manufacturing processes.
For example, a food processing plant can use Ignition to create a Digital Twin for their bottling line. By integrating PLC data,they can analyze the fill levels,speed variances,and maintenance schedules to optimize throughput and minimize downtime.
Q: How can Ignition integrate PLC data into a Digital Twin?
A: Ignition seamlessly connects to various PLCs, allowing you to extract data using the following methods:
- Direct OPC Connections: Use OPC UA to connect ignition directly to PLCs for real-time data exchange.
- Tag Configuration: Configure tags within Ignition to represent data points and commands from PLCs.
- Historical Data Logging: Leverage Ignition’s historian to log and retrieve data for trend analysis.
For instance, in a steel fabrication plant, PLC readings on temperature and speed can be integrated into a Digital Twin to help operators simulate adjustments to reduce energy consumption while maintaining product quality.
Q: What are some deployment pitfalls when building a Digital Twin with Ignition?
A: There are several common pitfalls to be aware of:
- Data Overload: Attempting to integrate too much data at once can complicate the system. prioritize critical data points.
- Scalability Concerns: Ensure your digital twin architecture can scale with operational demands and increasing data volume.
- Integration Complexity: Ensure compatibility between Ignition,PLCs,and other IT systems to avoid interaction issues.
In the automotive industry, a supplier might find that overwhelming their Digital Twin with non-essential data leads to more troubleshooting rather than insights. Streamlining data flow can prevent this.
Q: Can you provide a step-by-step approach to deploying a Digital Twin with Ignition?
A: Certainly.Here’s a high-level approach:
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with the Digital Twin. Is it efficiency,risk mitigation,or predictive analytics?
- Data Mapping: Identify key PLC data points needed for your Digital Twin and organize them using Ignition’s tag system.
- Connectivity: Set up OPC connections to your PLCs to ensure seamless data flow into Ignition.
- Visual Representation: Use Ignition’s Outlook or Vision modules to create intuitive dashboards and mimic operational processes.
- Testing and validation: Verify that your Digital Twin accurately reflects real-world operations. Use simulation to test its functionality.
- Iterate and Scale: Continuously refine your model as you incorporate feedback and expand operations.
By following this structured approach, a plastic manufacturing company can implement a digital Twin for its extrusion process, enhancing material accuracy and reducing waste substantially.
In Summary
building a digital twin using Ignition and PLC data unlocks a myriad of opportunities for manufacturers to enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and innovate with confidence. Key takeaways from this journey include:
- Seamless Integration: Utilizing Ignition’s robust capabilities to integrate with various PLCs ensures a harmonized system that mirrors the physical operations into the digital realm.
- Real-Time Analytics: Leverage real-time data analytics to drive informed decision-making and proactive maintenance strategies.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Ignition’s modular architecture allows manufacturers to start small and scale their digital twin initiatives as needed, ensuring alignment with buisness goals and technological advancements.
At Innorobix, we pride ourselves on decades of experience in crafting comprehensive Ignition solutions that not only meet immediate needs but also position organizations for future success. We invite you to explore how our expert team can tailor bespoke solutions for your unique challenges. Whether you’re looking to enhance system integration, optimize data flow, or explore new possibilities with a digital twin, Innorobix is your trusted partner.
Connect with us today to schedule a demo or consultation. Discover firsthand how our Ignition expertise can transform your manufacturing operations into a beacon of efficiency and innovation.