Introduction
In today’s fast-evolving technological landscape, municipal water plants are continually tasked with the challenge of maintaining operational efficiency while ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. Many facilities still rely on outdated SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, which not only impede real-time operational insights but can also hinder a facility’s ability to respond swiftly to critical events.
Replacing obsolete SCADA systems with modern solutions is not just a matter of upgrading technology; it’s about enhancing operational integrity, sustainability, and performance efficiency.This transition is vital for securing water quality, optimizing resource management, and adapting to increasing environmental concerns.
Key Considerations in Upgrading SCADA Systems:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to EPA standards for water quality monitoring and reporting.
- Data Accessibility: Transitioning from siloed data environments to integrated platforms that offer real-time access.
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing advanced analytics to identify potential equipment failures before they occur.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Implementing intuitive dashboards that facilitate operational monitoring without extensive training.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly linking existing plant processes and equipment with new technologies for holistic management.
Such as, cities that have successfully implemented modern SCADA systems report improvements not only in operational efficiency but also in public transparency and accountability. In this article, we will delve deeper into the numerous benefits of replacing obsolete SCADA systems and provide guidance on how to navigate this critical transition effectively.
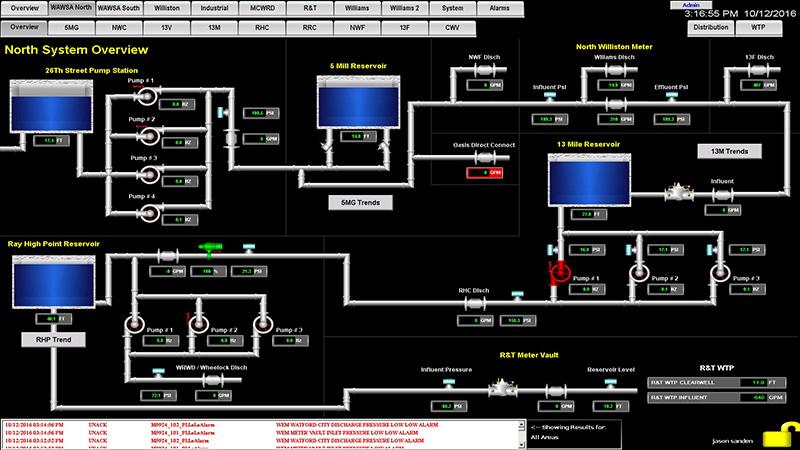
Assessing the Limitations of Existing SCADA Systems in Municipal Water Operations
Many municipal water operations still rely on legacy SCADA systems that were designed decades ago,lacking the capabilities and flexibility required for today’s dynamic water treatment environments. These outdated systems often suffer from limitations that hinder operational efficiency and can pose notable risks. Common issues include:
- Inadequate Data Management: Legacy SCADA systems frequently struggle with the volume and variety of data generated from modern water treatment facilities, leading to information silos that complicate decision-making.
- Poor Integration Capabilities: The inability to seamlessly integrate with newer technologies or third-party sensors can restrict operators from leveraging advanced analytics tools, ultimately leading to less optimized operations.
- Limited remote Access and Monitoring: With the growing need for remote work, these systems frequently enough lack secure remote access, making it challenging for operators to monitor systems or troubleshoot issues from off-site.
A case in point is a mid-sized municipal water plant that continued to use a SCADA system developed in the late 90s, putting them at a pronounced disadvantage. During a summer drought, operators faced difficulties tracking real-time water flow and pressure due to the outdated software’s inability to handle new sensor data.As a result, the facility was unable to efficiently allocate resources, leading to service disruptions and increased operational costs. Transitioning to a modern SCADA solution enabled this facility to integrate IoT sensors, which provided real-time data visualization and analysis that improved decision-making and resource management. Adopting such advanced systems allows municipalities not only to enhance operational reliability but also to significantly contribute to regulatory compliance and environmental sustainability.
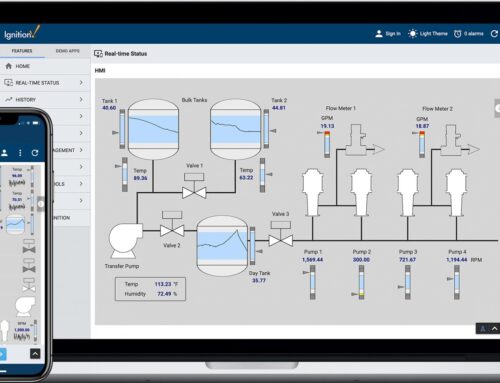
Identifying Key Features and Technologies for Modern SCADA Solutions
Modern SCADA solutions for municipal water plants are built on a foundation of cutting-edge technologies that enhance operational efficiency, data accuracy, and compliance with regulatory standards. Key features such as real-time monitoring, advanced data analytics, and cloud integration empower water utility managers to make informed decisions swiftly. For instance, the implementation of IoT sensors allows for remote data collection from various points in the treatment process, which data is then relayed to a centralized control system. This seamless integration enables operators to monitor water quality parameters, flow rates, and system status at any time from a user-friendly dashboard, significantly reducing the reliance on manual inspections.Furthermore, the ability to predict equipment failures through predictive analytics not only maximizes uptime but also extends the lifespan of critical assets.
Additionally, modern SCADA systems leverage the power of data visualization and mobile accessibility. By utilizing arcGIS technology, operators can visualize system layouts and regional water source maps in real time, improving situational awareness during emergency scenarios. With mobile applications, field technicians can access live data and receive alerts directly on their smartphones or tablets, enhancing responsiveness. Key components that should be included in an upgraded SCADA system are:
- Robust cybersecurity measures: Protecting sensitive data from potential cyber threats.
- Modular architecture: Facilitating scalability to adapt to future needs or expansions.
- Environmental compliance reporting tools: Ensuring adherence to local water quality regulations.
- Automated reporting features: Streamlining the generation of required operational and financial reports.
Implementing a Strategic upgrade Plan: Best Practices and Considerations
When embarking on the journey to replace obsolete SCADA systems in municipal water plants, it is indeed crucial to implement a well-defined upgrade strategy that incorporates proven best practices and thorough considerations.Conducting a comprehensive needs assessment should be the first step, examining both current operational challenges and future technology requirements. For instance, Ohio’s [City Name] faced frequent system outages due to outdated technology; their solution involved assessing key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure the new SCADA system could adequately handle real-time data processing and monitoring. This assessment not only revealed performance gaps but also guided them in selecting a platform that aligned with their long-term sustainability goals.
Furthermore, stakeholder engagement throughout the process cannot be overstated. Involving operators, management, and IT staff ensures that the system meets both operational needs and user requirements. Here are some key points to consider:
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation to track requirements and decisions throughout the upgrade process.
- Training: Incorporate comprehensive training programs for staff to facilitate smooth transitions to the new system.
- Testing: Implement staged testing of the new SCADA system to ensure all modules function as expected before full-scale deployment.
- Integration: Plan for integration with existing systems to avoid disruptions; real-world examples highlight the success of modular upgrades in facilities that phased out legacy systems.
These strategic approaches not only minimize downtime during the transition but also pave the way for improved operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards.
Ensuring Compliance and Future-Readiness through enhanced Data Management
The transition from outdated SCADA systems to modern data management solutions is critical for municipal water plants aiming to meet environmental regulations and prepare for future challenges.Enhanced data management facilitates real-time monitoring and streamlined reporting processes, ultimately driving operational efficiency. For example, the integration of advanced analytics enables the identification of anomalies in water quality, which can trigger automated alerts to operators. This not only improves response times but also minimizes the risk of regulatory non-compliance. A water treatment facility in california recently implemented a new data management system that reduced incident response time by 30%, ensuring they meet stringent safety standards imposed by the EPA.
Moreover, robust data management systems support comprehensive environmental reporting and data visualization, making compliance audits more straightforward. Operators can easily generate reports that outline water quality, chemical usage, and waste management practices, fulfilling regulatory requirements efficiently. Key features include:
- Automated Reporting: Streamline the creation of necessary compliance documentation.
- Data Visualization Tools: Utilize dashboards to present real-time metrics on operational performance and environmental impact clearly.
- Predictive Maintenance: Leverage past data to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan.
Water utility companies that adopt these modern solutions not only enhance compliance capabilities but also create a lasting framework for future growth and governance in an ever-evolving regulatory landscape.
In Conclusion
In closing,transitioning from obsolete SCADA systems in municipal water plants is not merely an upgrade; it is a strategic move towards enhanced efficiency,reliability,and compliance with modern regulatory standards. Key takeaways from our discussion include:
- Improved Data Integrity: New systems provide real-time data accuracy, reducing errors in monitoring and reporting.
- Enhanced User Interfaces: Modern SCADA solutions deliver intuitive interfaces, simplifying operations and reducing training time for staff.
- Robust Analytics Tools: Advanced analytics enable effective monitoring of system performance, optimizing maintenance schedules, and predicting potential failures.
- Seamless Integration: Upgraded systems can easily integrate with existing technology, providing a cohesive approach to water management.
As the demands for sustainable and efficient water services grow, investing in contemporary SCADA solutions becomes imperative. We invite you to explore innovative solutions with Innorobix or request a consultation/demo to see firsthand how upgrading your system can revolutionize your operations and enhance service delivery. Let’s work together to ensure your water plant is equipped for the future.