How to Digitally Track Scrap and Rework in Automotive Plants
In the highly competitive automotive manufacturing sector, efficiency and quality are paramount. Every scrap part and reworked unit not only translates into added costs but also jeopardizes delivery timelines and customer satisfaction. As automotive manufacturers strive for operational excellence, digitizing the tracking of scrap and rework has emerged as a vital strategy.Digital tracking solutions, empowered by robust systems such as Ignition and MES (Manufacturing execution Systems), enable manufacturers to gain insights that help reduce waste, streamline operations, and enhance overall product quality. Implementing these solutions can considerably transform how scrap and rework are managed, ultimately leading to improved productivity and profitability.
Why Focus on Scrap and Rework Tracking?
To grasp the importance of digital tracking in scrap and rework management, consider the following points:
- Cost Reduction: Every scrap part represents lost materials and additional labor for rework. Accurate tracking allows for timely interventions and cost-saving measures.
- Quality Enhancement: Understanding the reasons for scrap and rework can lead to quality enhancements in the production process, reducing future occurrences.
- Data-Driven decisions: Real-time data analysis helps identify trends, root causes, and areas for improvement, enabling informed decision-making.
Real-World Applications in Automotive Plants
- Identify Scrap Patterns: A leading automotive manufacturer implemented an MES system integrated with real-time data analytics, which enabled them to pinpoint specific production lines generating higher scrap rates. This insight allowed them to refine processes, cutting scrap by 20% within a year.
- Monitor Rework Trends: By deploying digital tracking tools, another automotive plant was able to monitor rework issues in real-time. They discovered that a common fault in a particular component was responsible for more than 30% of their rework instances. This discovery led to a focused quality control initiative, resulting in a 15% reduction in rework needs.
- Enhance Accountability: Digital tracking software ensured openness and accountability among teams, as employees could now log and track scrap and rework data in real time.This led to improved morale and a collective effort to minimize waste across the board.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the methodologies, tools, and best practices for effectively tracking scrap and rework in automotive plants, using practical examples and innovative strategies. By harnessing the power of digital solutions,manufacturers can not only mitigate waste but also drive continuous improvement across their operations.
Methods for Implementing Real-Time Scrap and Rework Tracking Systems
Implementing real-time scrap and rework tracking systems in automotive plants involves the integration of advanced technologies and well-defined processes to ensure accurate data collection and analysis. One effective method is the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices to monitor production lines continuously. By deploying sensors on machinery, manufacturers can capture data related to quality issues and equipment performance in real time. As a notable example, an automotive manufacturer such as Toyota has utilized this technology on their assembly lines to detect deviations from optimal performance. When a defect is identified, the data automatically triggers alerts to the responsible operators and updates the MES (manufacturing Execution System) database, allowing for immediate corrective action while also tracking scrap data for root cause analysis.
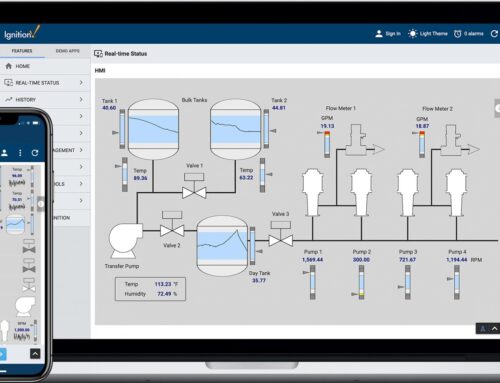
Additionally, leveraging cloud-based platforms for data consolidation enhances visibility and accessibility of information across the manufacturing process. With systems like Ignition, manufacturers can create dashboards that visualize real-time data related to scrap and rework, providing insights into operational efficiency. Key features of these systems include:
- Automated reporting features that summarize scrap rates per production batch.
- Customizable kpis that help identify trends and anomalies related to rework processes.
- Integration with PLCs (programmable Logic Controllers) and HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) to standardize data inputs across different production lines.
An example can be seen in Ford’s use of an integrated MES system that captures real-time data from multiple assembly plants, enabling them to analyze scrap metrics across their network, thereby driving continuous improvement initiatives. This systematic approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also lays the groundwork for digitizing traceability of every defective part throughout the entire supply chain.
Best Practices for Data Collection and Management in Automotive Manufacturing
Implementing an effective data collection and management system in automotive manufacturing can drastically improve the tracking of scrap and rework processes. One proven method involves using Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) integrated with Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems like Ignition.For example, a leading automotive plant in Michigan recently deployed Ignition to monitor real-time production data and track scrap rates directly on the factory floor. By utilizing custom dashboards, operators can instantly visualize data related to specific production lines, highlighting areas where materials are excessively scrapped or require rework. This immediate access to information empowers teams to investigate the root causes of inefficiencies, allowing for swift corrective measures to be implemented.
To enhance data accuracy and facilitate more insightful analysis, manufacturers should adopt standardization across all production lines. This standardization can include adopting uniform data collection protocols and PLC/HMI configurations, ensuring that scrap and rework metrics are consistently captured and reported. For instance, a prominent automotive manufacturer established a cross-line data management protocol that incorporates real-time feedback from multiple lines into their centralized MES system.This enables analytics teams to aggregate data for comprehensive reporting, helping to identify trends across various models and processes. Best practices include:
- Utilizing automated data capture methods to minimize human error.
- Implementing standardized reporting templates to maintain consistency.
- Regularly reviewing data integrity through audits and validation processes.
This strategic approach not only enhances traceability but also plays a crucial role in improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by focusing on continuous improvement across all manufacturing operations.
Leveraging Ignition and MES for enhanced Traceability and Reporting
In the realm of automotive manufacturing, tracking scrap and rework processes presents a critical challenge that can significantly impact overall efficiency and profitability. By integrating Ignition and a Manufacturing Execution System (MES), plants can achieve a high level of traceability that directly addresses these issues. Such as,one major automotive manufacturer implemented an Ignition-driven MES to monitor scrap rates on the shop floor in real time.This integration enabled operators to visualize scrap patterns by linking data from various production lines, allowing them to identify recurring issues, whether from specific machines or shifts. As a result, they were able to proactively implement corrective measures, which reduced scrap rates by over 20% within a quarter.
furthermore, the MES provides robust reporting capabilities that enhance decision-making processes related to production quality.Utilizing Ignition’s built-in reporting tools, automotive plants can generate detailed reports on scrap and rework metrics, enabling stakeholders to assess not just volume but also the types of defects leading to rework. this data can then be cross-referenced with machine performance and operator efficiency to pinpoint areas of improvement. By leveraging this systematic approach, organizations can standardize traceability processes across all assembly lines, ensuring that quality control measures are consistently applied. The integration not only strengthens accountability but also aligns with regulatory demands, positioning the facility as a leader in quality management and operational excellence within the industry.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Scrap Reduction and Process Improvement in Automotive Plants
In a leading automotive manufacturing facility, the implementation of a digital tracking system through Ignition and advanced MES systems resulted in a 35% reduction in scrap rates within the first six months. This automotive plant highlighted the effectiveness of integrating real-time data capturing mechanisms on the production floor. Utilizing connected sensors, operators could now identify defects and deviations in the manufacturing process immediately, allowing for swift corrective actions.With digitized traceability, every unit moving through the production line was monitored, and discrepancies were logged into the system, which facilitated a detailed analysis of scrap origin, enabling targeted process improvements. The plant also developed key performance indicators (KPIs) correlated with the data insights, ensuring management could keep a continuous pulse on production efficiency and scrap reduction efforts.
Another exemplary case involves a prominent electric vehicle manufacturer that standardized their PLC and HMI interfaces across all production lines. By implementing a unified control strategy utilizing Ignition, operators at this facility could leverage comprehensive dashboards that provided visibility into scrap and rework metrics in real-time. This method not only enhanced the operator’s ability to act swiftly to mitigate issues but also facilitated team collaboration on process reviews. The introduction of automated alerts for deviations from quality standards further streamlined the process, resulting in a 20% reduction in rework. Key improvements included enhanced operator training programs, informed by real-time data analytics that showcased patterns in scrap generation, equipping teams to proactively address potential weaknesses in the manufacturing process.
Closing Remarks
effectively tracking scrap and rework in automotive plants is essential for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing waste. By implementing a robust digital system, manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in quality control and resource management. Key takeaways from this discussion include:
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Utilizing advanced SCADA systems and MES solutions allows for real-time visibility into scrap and rework metrics, enabling swift corrective actions.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Streamlining your processes by integrating MES with existing ERP and PLC systems fosters seamless interaction across the production floor.
- Data-Driven decision Making: leveraging analytics capabilities helps identify patterns and root causes of scrap, facilitating continuous improvement initiatives.
- Standardization Across Operations: Adopting uniform metrics and methodologies across all production lines enhances traceability and accountability.
By embracing these strategies, automotive manufacturers can significantly reduce downtime, improve Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE), and enhance their competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving industry.We invite you to explore innovative solutions with Innorobix that can elevate your operations.For further insights or to schedule a personalized consultation or demo, please reach out to our experts today.Together, we can transform your manufacturing processes for the future.