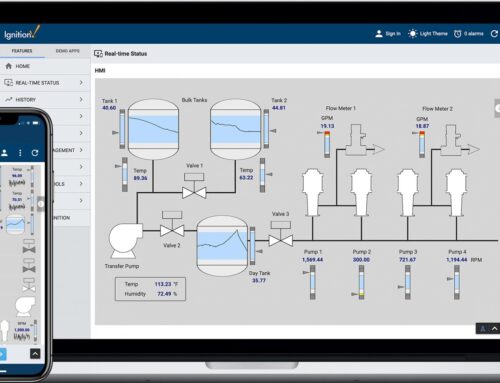
Introduction: Automating Chemical Dosing Systems Using Flow Logic
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation, chemical dosing systems stand as a critical component across various sectors, including water treatment, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food processing. The precision and reliability of chemical dosing not only ensure product quality and compliance with regulatory standards but also play a pivotal role in operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This article delves into the sophisticated realm of automating these systems through the implementation of flow logic,illustrating the substantial advancements and opportunities that come with this technological integration.
Key Benefits of automation in Chemical Dosing Systems:
- enhanced Precision: Automation minimizes human error, delivering exact quantities of chemicals necessary for each specific process.
- Efficiency Improvements: streamlined processes reduce the time required for chemical dispensing, leading to faster production cycles.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Automated systems optimize chemical use, considerably reducing waste and associated costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Consistent dosing supports adherence to stringent industry regulations regarding chemical usage and safety.
Flow Logic: The Foundation of Automation
Flow logic is the backbone of automated chemical dosing, allowing for the seamless integration of data inputs to make informed decisions in real-time. Its request involves:
- Sensor Integration: Utilizing flow meters and level sensors to gather accurate data regarding chemical flow rates and tank levels.
- Controller Programming: Designing control logic using programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to manage dosing operations based on real-time sensor feedback.
- Adaptive Algorithms: Implementing algorithms that adjust dosing rates automatically in response to process variations.
Examples of Flow Logic Enhancements:
- Adaptive Dosing: introducing PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to adjust chemical flow rates dynamically,maintaining desired concentration levels even with fluctuating input conditions.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Utilizing SCADA systems for real-time monitoring and remote control of dosing operations, allowing operators to intervene swiftly if anomalies are detected.
- Alarm Systems: Setting up automated alarms to notify operators of potential issues, such as unexpected changes in flow rates or tank levels, ensuring rapid response to avoid process disruptions.
Through the strategic implementation of flow logic in automating chemical dosing systems, industries can achieve unprecedented levels of operational excellence. This article will further explore detailed methodologies, case studies, and recommendations for professionals aiming to harness the full potential of automation in their chemical dosing applications. With insightful examples and comprehensive strategies,our goal is to equip readers with the knowledge to drive efficiency and innovation in their respective fields.
understanding Flow Logic for Accurate Chemical Dosing Systems
Accurate chemical dosing is critical in industries ranging from water treatment to pharmaceuticals, where precision determines efficacy and safety. Flow logic is a systematic approach that ensures the correct chemical dosage is administered at the right time, based on real-time conditions. This logic utilizes feedback from flow sensors and analyzers to adjust the dosing mechanism dynamically. As a notable example, in a water treatment plant, sensors detect variations in water flow and quality. The flow logic adjusts chemical pumps accordingly to maintain optimal pH levels and contaminant reduction. This real-time adjustment minimizes waste and enhances system efficiency, essential for compliance with environmental regulations.
To implement effective flow logic, consider the following key components:
- Real-time Monitoring: Use sensors to constantly measure flow rates, pH levels, and other relevant parameters.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Integrate PLCs to interpret sensor data and adjust dosing rates automatically.
- Feedback Loops: Implement closed-loop control systems that continuously evaluate performance and make iterative adjustments.
- User Interface: Provide operators with a clear dashboard to monitor processes and make manual adjustments if necessary.
- Data Logging: Ensure all adjustments and sensor readings are logged for review and compliance purposes.
Real-world examples like beverage production benefit from precise carbonation levels, achieved through intelligent flow logic, ensuring product consistency and taste. Accurate flow logic transforms chemical dosing from a manual, error-prone process to an automated, precise system, driving productivity and sustainability.
Implementing Sensor-Based Automation for Precise Chemical Control
Sensor-based automation in chemical dosing systems leverages advanced sensors and control technologies to ensure optimal chemical concentrations. Instead of relying on manual adjustments, sensors such as pH probes, conductivity meters, and turbidity sensors continuously feed real-time data to a centralized control system. This approach enables precise monitoring and control, adjusting the dosing pumps according to the deviations detected in the process stream. As an example, in water treatment facilities, sensor-driven feedback loops can regulate chlorine levels to meet safety standards without overuse, reducing both the cost and environmental impact. Key advantages include improved accuracy and the ability to handle large volumes of data seamlessly, ensuring more consistent chemical reactions and treatments.
Integrating flow logic with these sensors adds another layer of sophistication. Flow meters measure the volume and rate of chemicals passing through the system, which allows the implementation of logic algorithms that determine the exact amount of chemicals needed based on calculated flow rates. Real-world practicalities include:
- Enhanced safety by preventing under or overdosing, crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals where specific chemical interactions are critical.
- Cost savings through reduced chemical waste and minimized need for human intervention.
- Scalability and flexibility, allowing systems to easily adjust to changing requirements or integrate additional process parameters.
By deploying sensor-based automation with flow logic, industries can achieve a higher standard of chemical process control, leading to improved product quality and operational efficiency.
Configuring Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustments in Dosing Processes
Real-time monitoring in chemical dosing processes allows for precision and adaptability, vital for industries where dosage accuracy impacts the efficacy and safety of operations. Integrating sensors within the dosing lines that measure flow rate, temperature, and pressure can dramatically enhance the process by providing continuous feedback. This data feeds into a centralized control system, frequently enough a PLC or SCADA, which Ignition can interact with to offer a detailed, real-time view of the dosing process. Such as, a water treatment facility may use flow meters and pH sensors to ensure the correct amount of chemical is dispensed, immediately adjusting based on sensor feedback to maintain optimal pH levels. This not only helps in maintaining product quality but also reduces chemical waste, directly contributing to cost efficiency and environmental goals.
To facilitate seamless adjustments, flow logic algorithms can be implemented within Ignition to automatically modify dosing parameters. Such algorithms may incorporate past data trends and predictive modeling to preemptively adjust dosages in anticipation of changes in process conditions, such as fluctuating demand or raw material variability. For instance, in the food and beverage industry, where viscosity changes can affect fluid flow dynamics, Ignition’s real-time analytics can ensure that pumps adjust flow rates dynamically, ensuring consistent product quality. Key strategies include:
- Using historical and current process data to model optimal dosing patterns.
- Implementing predictive maintenance alerts to minimize unplanned downtime.
- Providing operators with actionable insights through intuitive dashboards and alerts, enabling immediate manual intervention if required.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Safety in Automated Chemical Dosing Systems
Maintenance and safety stand as cornerstones of effective operational strategy in automated chemical dosing systems. Regular calibration of dosing equipment ensures precision in chemical delivery, reducing the risk of under- or over-dosing which can lead to significant operational disruptions or safety hazards.As a notable example, calibrating flow sensors biweekly not only prolongs their lifespan but also maintains dosing accuracy, thereby safeguarding product quality. Implementing preventive maintenance schedules can mitigate unexpected breakdowns. This includes routine checks on connections, seals, and pressure levels, especially in high-use systems where wear and tear are more prevalent. Training staff to understand these procedures and recognize early signs of equipment failure—such as unusual noise or pressure drops—is crucial. By using a combination of regular equipment audits and employee training,companies can maintain operational integrity and safety.
Safety protocols must extend beyond the machinery to encompass the entire operational process. Establishing clear emergency protocols for handling chemical spills is indispensable. These protocols should include spill containment strategies,employee evacuation routes,and dialog plans to trigger alarms and summon emergency response teams swiftly.Incorporating automated safety interlocks that halt operations if irregular conditions are detected—like pressure anomalies or valve failures—can avert accidents before they happen. Real-world examples show that interlocking systems can prevent equipment damage and personnel injury by shutting down pumps when leak detection systems sense an anomaly. Moreover, providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensuring its consistent use can protect employees from accidental exposure to harmful chemicals. Regular safety drills, alongside these implementations, enhance preparedness and confidence in dealing with potential hazards, creating a safer and more efficient work surroundings.
To Conclude
the automation of chemical dosing systems using flow logic represents a significant advancement in process optimization,safety,and efficiency within industrial settings. Key takeaways include:
- Precision and Accuracy: Automated systems ensure consistent dosing, minimizing human error and optimizing resource use.
- Enhanced Safety: Flow logic integration reduces the risk of chemical exposure and potential accidents, safeguarding personnel and equipment.
- Increased Efficiency: Real-time monitoring and adjustments lead to more efficient operations and reduced downtime.
- Scalability and Flexibility: These systems can be tailored to suit varied operational needs and easily adapted as those needs evolve.
By leveraging the capabilities of advanced technologies and intelligent automation, organizations can not only enhance operational performance but also ensure compliance with environmental and safety regulations. We invite you to explore how innorobix can deliver tailored solutions to meet your specific needs. Contact us to request a consultation or schedule a demo, and see firsthand how flow logic can transform your chemical dosing processes.